Whether your passion is to reduce human suffering from disease, mitigate climate-change effects on ecosystems, or advance how we understand, explain and predict living systems, your career will benefit from the unique competitive advantages of a QSB degree.
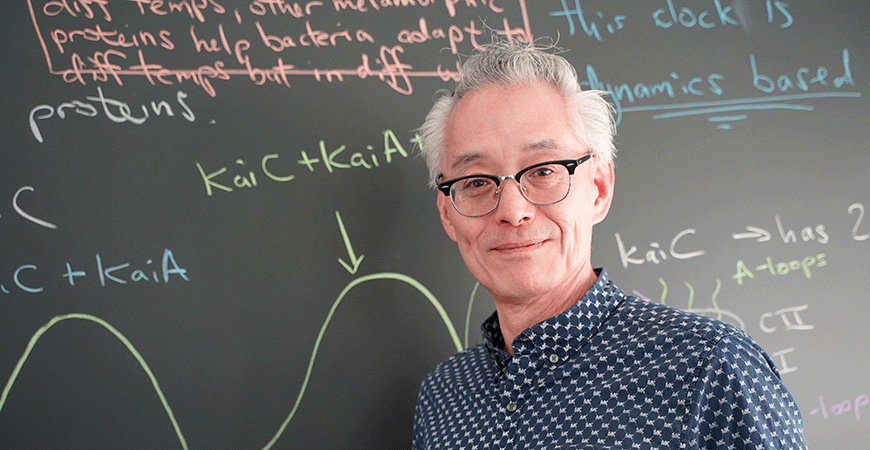
Biochemistry Professor Andy LiWang has spent much of his career studying how life keeps time. His work on the circadian clock of cyanobacteria — tiny, ancient organisms that share the planet with us...

UC Merced continues to demonstrate its growing influence on the global stage. Several faculty members landed on Clarivate’s 2025 list of the world’s most‑cited researchers. The honor is reserved for...

The same cellular renewal that keeps our bodies healthy might also fuel the growth of cancer. A UC Merced biologist has found that the brain could hold the key to stopping it. Professor Néstor Oviedo...